Mac X Network Traffic Command - NETTOP
If you are like any IT professional today, you're concerned about security. Mac OS X has it's own Terminal utility called nettop that monitors incoming/outgoing network connections. This might remind you about Windows "netstat" utility.
Immediately, nettop will output every connection coming in and out of your NIC's. The information will be displayed in Terminal. Nettop can be used with several arguments, shown further down this article, to help reduce cpu load and to inspect other traffic (UDP/TCP) insightfully.
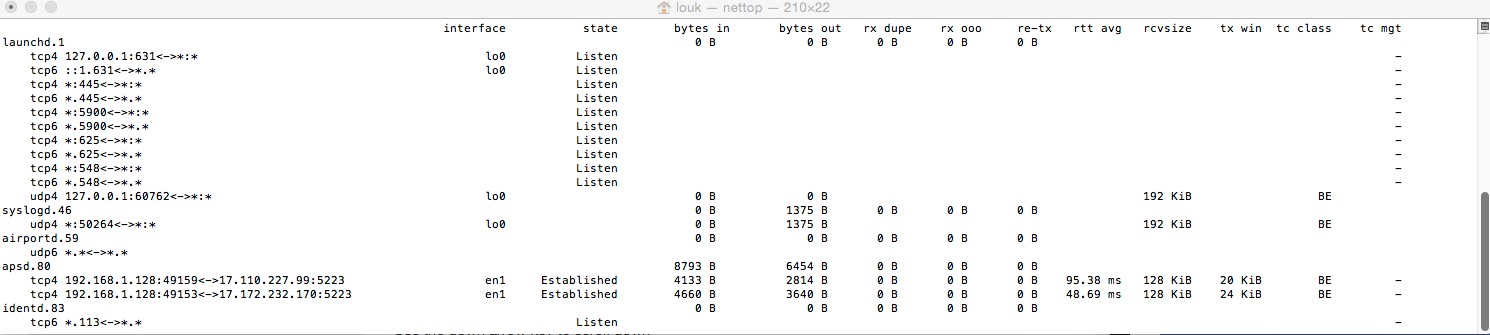
You can have NETTOP running 24/7 and dumping to a text file which I check weekly. Depening how much traffic you generate, you might want to do this to - so anyone already accessing your computer files stealthly you might be able to track (hide NETTOP directory for this reason too)!
ARGUEMENTS:
NAME nettop -- Display updated information about the network SYNOPSIS nettop [-nc] [-m ] DESCRIPTION The nettop program displays a list of sockets or routes. The counts for network structures are updated periodically. While the program is running the following keys may be used: q Quit Up Arrow Scroll up Down Arrow Scroll down Right Arrow Scroll Right Left Arrow Scroll Left d Toggle delta output r Redraw screen p Toggle human readable numbers e Expand all c Collapse all h Bring up the help menu j Bring up the column selection menu. In this mode you can enable/disable columns and change their order. OPTIONS A list of flags and their descriptions: -m Specify the mode. By default, nettop will monitor TCP and UDP sockets. The following modes are supported: tcp Only TCP sockets will be monitored udp Only UDP sockets will be monitored route Instead of sockets, the routing table will be monitored -n Disable address to name resolution
-c Less intensive use of the CPU - draws less often

Comments 1
Mac OS X has its* own